An introduction to Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed database or public ledger recording all the transactions on the network. The idea of Blockchain is old but it came into practice with Bitcoin and all the new cryptocurrenices are based on this technology. It was revealed by Nakamoto in their paper ““Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”. There are three core parts of Blockchain:
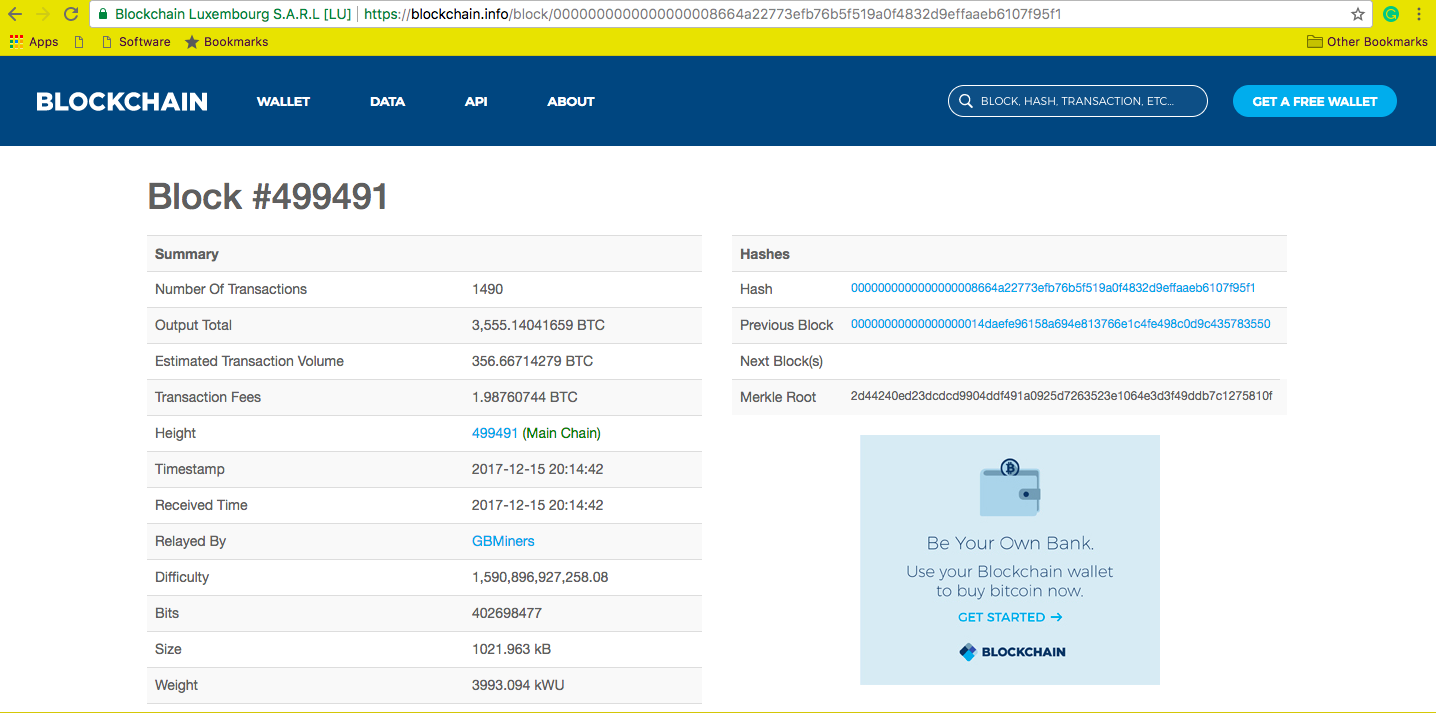
1- Block
A block is a list of transactions recorded over a specific period of time and this time period depends on the protocol of the cryptocurrency. Each currency has different time of adding a new block to its Blockchain.
2- Chain
A new block of transactions is added to the previous block and this is how a chain of blocks is created. This is done by hashing. A mathematical algorithm maps data of any size into a fixed length size of bit string and this algorithm is created by hash function which will be discussed in detail in hashing function. This bit string then represents the data that was hashed. The most common cryptographic algorithm used in Blockchain is secure hash algorithm (SHA). The SHA 256 is an algorithm that maps data to a unique 256 bits (32 bytes) string. The time of adding a new block to previous block depends on a cryptocurrency protocol. All cryptocurrencies have their different protocols for running the Blockchain.
3- Network
Blockchain has a network of computers known as full nodes. These computers run a specific Blockchain algorithm to run and secure network. These nodes have a complete record of all the transactions ever made on the Blockchain. If you download the software of a particular cryptocurrency, your computer will also become a part of the network.
Types of blockchain
There are three distinct types of Blockchains.
1- Public Blockchain:
Public blockhain are open source software and distributed widely. Anyone from public can participate in such Blockchains such as bitcoin. A native token runs these Blockchains. For example, in case of bitcoin Blockchain bitcoin currency is the native token.2- Permissioned Blockchain:
These Blockchain may or may not have open source code. Permissioned Blockchain controls the role of participants. These Blockchains are also largely distributed and run through a native token.3-Private Blockchains:
These Blockchains are for consortiums. Activities of users are strictly controlled in these Blockchains. The scale is smaller and limited to an organization. No token is used. These blockchains are used to share confidential information between trusted members.Why Blockchain is so important
Blockchain is considered the missing layer of trust for the internet and the “fifth evolution” of computing because participants do not have to trust each other to make a transaction.
Once a transaction is added to Blockchain it cannot be changed. It will stay on the ledger as long as Blockchain exists preventing deception.
Blockchain is not restricted for making payments but can also be used for recording any kind of data online securely which is a crucial need in this era of technology when hackers and thieves invent new ways of deception and hacking.
Everybody can see all the transactions but identity of the users is kept anonymous.
It has not only changed the traditional financial system but also has introduced new technologies such as smart contracts and decentralized organizations which will be discussed in detail later.
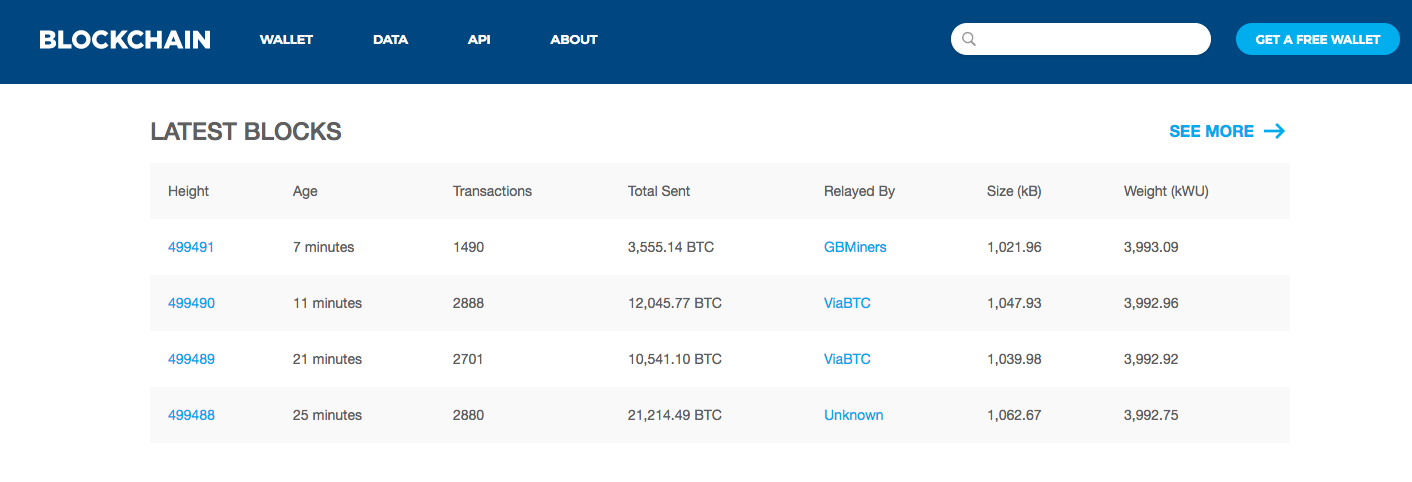
The most reliable website for seeing Blockchain blocks and transactions is https://Blockchain.info/
I found this book by Tiana Laurance very interesting and easy to comprehend. Anyone with an interest to get hands on Blockhain must read this book.