How bitcoins are created
The driving force for a Blockchain is its consensus. A consensus is a process of an agreement between participants. The consensus for bitcoin Blockchain is called proof of work. Proof of work is a protocol that shields the system against cyber-attacks such as denial of service attacks by creating complex mathematical problem known as proof of work problem for miners to solve.
Miners are the people who run Bitcoin software on their computers. Whenever a transaction is made, it needs to be verified by miners. All the nodes or computers have a ledger that needs to be updated after 10 minutes. All the miners compete to solve the problem and whoever solves the problem first announces to the entire network that they have found the solution. The miner who solved the puzzle first then verifies all the transactions occurred during those 10 minutes. This new block of transaction is distributed among all the computers and if more than 50% computers agree on the transactions made, a new block is added to the Blockchain.
Miners are rewarded by protocol with Bitcoins and this is how new Bitcoins are created, rewarding also creates an incentive for other people to mine. The technical detail behind mining will be discussed later.
Once a transaction is added to Blockchain it cannot be changed. It will stay on the ledger as long as Blockchain exists. The proof of work consensus for bitcoin is distributed and trustless meaning that unlike traditional payment system sender and receiver do not have to trust each other.
Benefits of bitcoin
Quick cheap and easy
There are number of benefits of this technology. First of all, sending money has become cheaper, quicker and easy. If we have to send money through our bank to someone in another country. It takes a lot of time as this money has to go thorough more than one banks and all the banks have their separate ledger and separate systems. Therefore, it takes time to get to receiver and also sender has to pay the costs of banks services but Bitcoin makes it easy as sender is directly sending money to the receiver. There is no long wait and no extra cost as the payment system is peer-to-peer.Trustworthy
Since Bitcoin uses a transparent ledger that is publically available to see and it keeps a record of all the transactions. Therefore, Bitcoin delivers a trustless solution because to make a transaction participants do not have to trust each other as the system itself is trustworthy. No one can cheat, as it will require a huge effort to hack all the computers running Blockchain. The Blockchain system assures that no money his spent twice. Due to its transparency people can put in their trust.Why bitcoin is valued
Bitcoin is considered as gold currency. Like any other currency its value lies in economics principles, utility, supply and demand.
Why is it in demand
This currency started to gain value because people put their trust in the currency. Bitcoin demand is high because of its utility. People can transfer money or pay for goods efficiently without any centralized authority and caring about international borders. Moreover, because of its increasing value people also buy Bitcoins as an asset like gold is bought because it has greater value.Wide use
Although, there are many cryptocurrencies available but Bitcoin is widely used and trusted. The digital currency is now accepted by thousands of merchants across the globe. As more and more people are becoming aware of Bitcoins and buying the currency, its value is increasing because it is widely accepted now.Scarcity
Bitcoin supply is limited as the software is designed in a way that only a limited number of Bitcoins can be mined. As of March 2017, there were 16.2m Bitcoins in circulation and maximum 21 million Bitcoins can be mined. The year expected for the end of mining Bitcoin is 2140 . If we apply the simple rule of economics, something that has a higher demand but limited supply, will have greater price.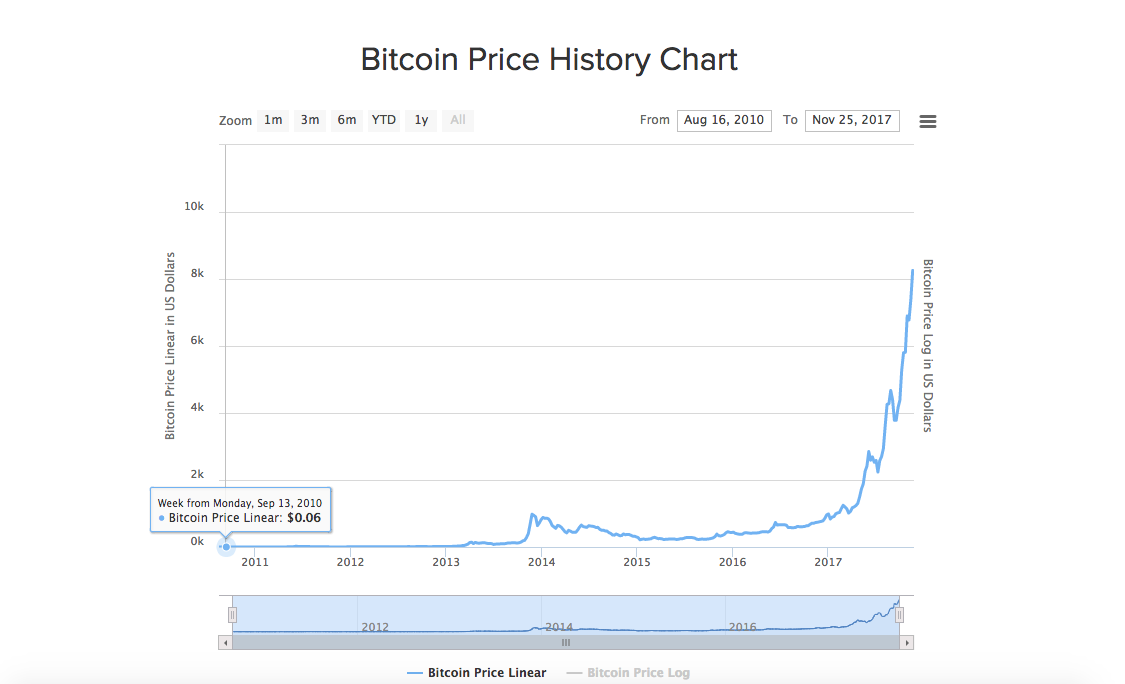
In 2009, Bitcoin value was $0 and in 2010 Bitcoin’s highest value was $0.39.
Issues with bitcoin
Although, bitcoin is leading the race of cryptocurrencies but it has some drawbacks too
Transaction time issue
A block is added to Bitcoin’s Blockchain after 10 minutes which results a transaction confirmation time of 10 minutes. A person can wait for 10 minutes if they are transferring money internationally, but this transaction time is very slow if one wants to pay for their grocery bills in a supermarket with Bitcoin.Scalability issue
The size of a block of Blockchain is 1MB. Only 7 transactions can be made per second which creates a scalability issue. This Blockchain size cannot be expanded because this is how the protocol is programmed. The demand of using Bitcoin Blockchain ledger is rising but Bitcoin cannot handle the volume of transactions.Promoting black money
Bitcoin has opened a door for black money as there is no centralized authority or government to control or surveil who is making transactions and what they are paying for because of the anonymity of the participants.About Us

Author
Contact me
IB279@live.mdx.ac.uk
